Fiber Optic Cable Range: How Far Will It Go
Are you curious about how far your fiber optic cable will go? This is a question that many people have, and it is a valid one. After all, you want to make sure that you are getting the most out of your investment. In this blog post, we will discuss fiber optic cable range and what factors affect it. We will also provide some tips on how to get the most out of your fiber optic cable range.
What are the main advantages of using fiber optic cabling?
Fiber optic cabling has many advantages over other types of cabling. It is much thinner than other types of cable, which makes it easier to install and less likely to be damaged. Fiber optic cabling is also much more flexible, which means that it can be used in a variety of applications. In terms of performance, you can expect higher bandwidth, higher speed internet, and greater reliability as some of the main advantages of using fiber optic cabling.
What fiber optic cable range do you need?
When planning the range required for your specific installation, consider:
- The length of cable run
- How much bandwidth you need now
- How much bandwidth you might need in the future.
Future proofing your fiber optic cable installation is vital to avoid costly re-cabling jobs down the line. And with installation costs often equalling the price of materials, it makes sense to install a future proofed fiber optic cable system to save you money and headaches in the long run.
How does fiber optic cable range work?
Fiber optic cable range is determined by a number of factors, the most important of which is attenuation. This term is the loss of signal strength that occurs as light travels through the fiber. The farther the light has to travel, the more attenuation will occur. Where possible, choose a fiber optic cable with a low attenuation rating.
Another important factor that affects fiber optic cable range is dispersion. This is where light waves travel at different speeds through the fiber, causing the light to spread out and eventually leading to signal degradation. Therefore, it is important to choose a fiber optic cable with a low dispersion rating.
What is the maximum distance of fiber optic cable?
Although the maximum distance of fiber optic cable is affected by both attenuation and dispersion, for most applications, the maximum distance of any type of fiber optic cable is around 62.14 miles (100 kilometers).
However, some applications require longer distances. For these applications, fiber optic cables with special dispersion-compensating fibers can be used. These cables can extend the maximum distance to around 124.28 miles (200 kilometers).
Is fiber-optic good for long distances?
Fiber optic cables are perfect for long-distance applications. They can carry information over very long distances with very little signal loss. Additionally, fiber optic cables are not affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for use in environments where EMI is a concern.
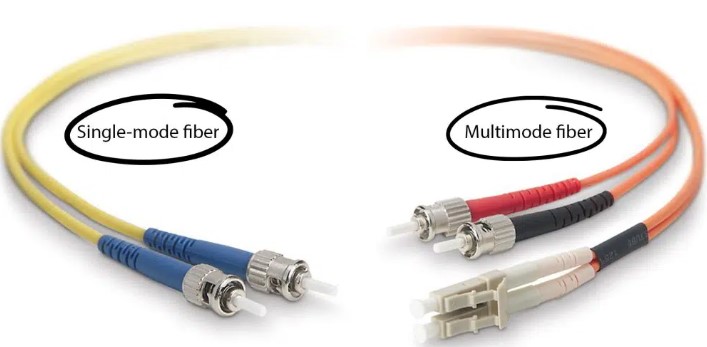
What is the maximum distance of single-mode vs. multimode fiber optic
There are two main different types of fiber optic cable: single-mode fiber and multimode fiber cable. Single-mode is typically used for long-distance applications, while multimode is typically used for short distances.
You’ll usually find multimode cabling used for the backbone or horizontal distribution in a LAN (local area network), while single-mode is for long-distance data transmission.
Let’s dig deeper into the numbers for full details of your fiber optic cable range.
- 1 GB/S Network – An OM1 cable will support 1000BASE-SX out to 275 meters, increasing to 550 meters if you use an OM2 cable. If you want to reach distances of 860 meters, it’s probably best to use single-mode cable rather than multi-mode.
- 10 GB/S Network – where 1000BASE-SX is insufficient, and you’re moving to a 10-gigabit network, you’ll need to consider using a higher-grade cable. An OM1 cable would have a distance of just 33 meters on a 10GBASE-SR network but offers 275 meters for 1000BASE-SX networks. Going up a level to the OM2 sees a 550-meter limit for 1000BASE-SX networks, dropping to 82 meters for the 10GBASE-SR network. While the OM3 multimode offers up to 300 meters. In comparison, single-mode cables can reach distances of 5km in a 1000BASE-SX setup.
- 40 and 100 GB/S Network – you’ll require an MPO-style connector for a 40GBASE-SR4 network. OM1 and OM2 cabling aren’t suitable here, but you can use OM3 and OM4. Expect distance limits of 100 meters and 150 meters, respectively. Your single-mode cable can achieve far greater distances of 10km at this level.
What is the maximum transmission distance of copper?
Fiber optic cabling is typically used as an upgrade to traditional copper cables, which are slower and less reliable than fiber optics. So, how much further is your fiber optic cable range in comparison to copper?
The maximum distance of copper is around 328 feet (100 meters) which is a far shorter range than is offered by either of the fiber optic cable types. This is because fiber optic cable is not affected by attenuation, dispersion, or EMI in the same way that copper is.
How can you get the most out of your fiber optic cable range?
If you want to make sure that you’re maximizing the potential of your fiber optic cable, it’s important to follow these tips:
- Make sure that your cable is properly installed and terminated.
- Inspect your cable regularly for any damage or signs of wear and tear.
- Use a high-quality cable from a reputable manufacturer.
Contact The Network Installers today
Do you have any questions or concerns about your fiber optic cable range? Our team are experts in fiber optic installation and would love to discuss your specific project. Get in touch with The Network Installers to receive our guidance and a free, no-obligation quote
Contact us Today!
ADDRESS
- Western Heights, 5th Floor, Karuna Close.
PAGES
- About US
- Our Services
- Blog
- Contact Us
